
We are dubious about the indications for arteriography, which is not always a risk-free examination, and therefore prefer doppler examination with ultrasound, which supplies adequate information in the majority of cases. Morrison, H., et al: A Study of the Dorsalis Pedis and Posterior Tibial Pulses in 1,000 Individuals Without Symptoms of Circulatory Affections of the Extremities, New Engl.

This pulse point's location can change depending on your patient's anatomy, but palpating for the pulse in the fossa (depression) just posterior to the medial malleolus is sufficient for most patients. 5 The dorsalis pedis is at the anterior aspect of the foot, lateral to the extensor hallucis tendon, and is generally within 1cm of the bony prominence of the navicular. The posterior tibial pulse is found behind the medial malleolus (the bony prominence on the inside of your ankle). Check for either the dorsalis pedis pulse (on the top of the foot) or the posterior tibial pulse (located behind the medial malleolus the ankle. Then palpate down this tendon and when you come to end of it, go to. To find this artery, locate the EHL (extensor hallucis longus) tendon by having the patient extend the big toe.
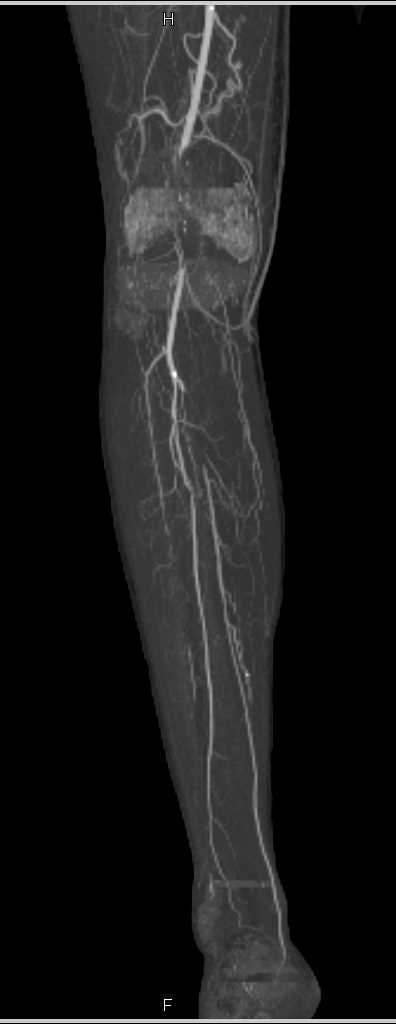
It is located immediately posterior to the medial malleolus. Two possible pedal pulse positions to check. The posterior tibial pulse point is found on the inside of the ankle between the medial malleolus (bony part of the ankle bone) and Achilles tendon. It is also a synergist of tibialis anterior in inversion of the foot. As a result, it helps with plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint. This muscle crosses the ankle joint to insert on the plantar surface of the foot. can be demonstrated by arteriography and doppler ultrasound. The posterior tibial pulse may be the most difficult to palpate, especially among less experienced clinicians. Tibialis posterior is hidden from view by the large, superficial muscles of the leg gastrocnemius and soleus. In practice, absence of the posterior tibial a. from the peroneal a., absence of the anterior tibial a., aplasia of the terminal portions of both the anterior and posterior tibial aa. Other anatomic variations may be found: trifurcation of the popliteal a., origin of the anterior tibial a. One study demonstrated increased interinvestigator agreement among 78 of posterior tibial pulses versus only 58 of the dorsalis pedis pulses when identified. 4), in which case the vascularisation of the fibula remains as normal (the proximal epiphysis of the fibula is vascularised by the anterior tibial a., the diaphysis and the distal epiphysis by the peroneal a.). The fibular artery was larger than usual and crossed the lowest portion of the interosseous membrane and continued as dorsalis pedis artery. is constant, for phylogenetic and embryologic reasons, 2) the posterior tibial a. Several findings emerged: 1) the peroneal a.
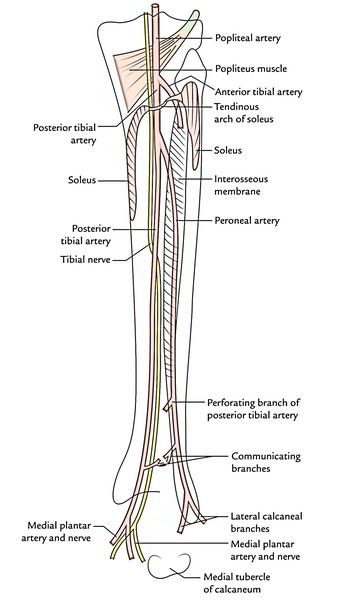
This study allowed classification of the origins of the leg arteries from the popliteal a. European J Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. We have studied 40 personal case-records of dissection of the arteries of the leg in fresh corpses. A Unique case of Superficial Posterior tibial artery- anatomical and clinical considerations. A well-documented case of absence of the posterior tibial a.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
